LED bulb FAQs
Look below for more detailed information about energy-efficient LED bulbs.
-
What types of LED lighting are available?
Currently, there are light fixtures, screw-in replacement bulbs, and decorative light strings that use LED bulbs. LED bulbs consume at least 80 percent less energy than conventional incandescent bulbs and last anywhere from 13-25 years longer.
-
Are LED lighting products dimmable?
Some are, but not all. LED bulbs and fixtures that are dimmable will specify on the packaging that these features are available, and they may not be compatible with dimmer fixtures or controls designed for incandescent bulbs. You may have to replace existing dimmer fixtures or controls with ones that are compatible with your LED lighting product.
Check the packaging or accompanying instructions to see if your LED bulb or fixture is dimmable and to find out which incandescent dimmer fixtures or controls are approved for use with the product. As the LED industry grows, fully compatible LED bulb and fixtures will become more prevalent in new construction. In the meantime, confirm with the LED lighting product manufacturer that your new LED bulb or fixture is compatible with your existing dimmer products.
-
Do LED lights create heat?
Yes, but not as much as other light sources. Incandescent and CFL bulbs produce heat that travels in the actual beams of light, much like the heat that comes from sunlight, and LED lights convert significantly less energy into this kind of heat. But the small amount of heat that LED lights do create can affect the quantity and quality of the light over time.
To combat the negative effects of heat on performance, LED product manufacturers incorporate heat sinks into their designs, through which heat is transferred away from the LED to another medium via conduction.
-
What colors of light are available for LED bulbs?
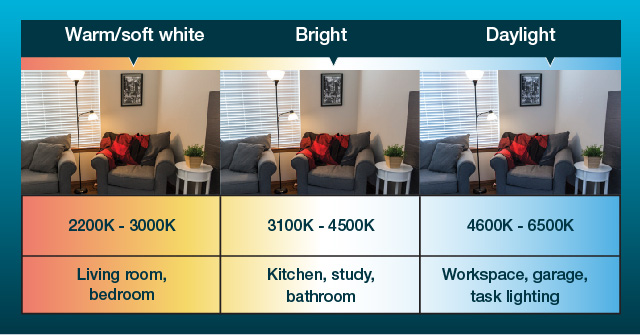
LED bulbs are available in a variety of shades of light that generally fall into three categories:
- "warm" light, a softer light that's comparable to the yellowish light of incandescent bulbs
- "bright white", a whiter light that's typically used for reading
- "cool" or "daylight," a slightly bluish light that's typically used for task or office work
On the color temperature scale, a lower Kelvin measurement means that the light appears more yellow. A higher Kelvin measurement means that the light appears more white or blue.
- To match the color of incandescent bulbs, look for bulbs between 2200 and 3000 K.
- For a whiter light, look for between 3100 and 4500 K.
- For bluer white light, look for bulbs between 4600 and 6500 K.
-
How do I pick the right LED bulb for my needs?
Follow these easy steps to choose your LED bulb.








